The Ultimate Guide for Service Innovation
Driving a winning pace in your service transformation & growth
Free Download
Read the guide later
Everything you need to accelerate and maintain your pace in your service innovation.
Download now and read later
Download your Free Guide to Your Service Innovation
Table of Contents
As industries transform and customer expectations evolve, manufacturers navigate an exciting and demanding transition from traditional operational aftermarket roles to strategic business lines.
A critical aspect of this transition is advancing their service offerings to maintain relevance and competitiveness. Elevating service innovation capabilities and practices is fundamental to their success in this evolving landscape.
Download your Free Guide to Your Service Innovation
What is service innovation
Definition
Service innovation is about changing how customers are served to create value for customers and the service provider.
It involves a combination of the following changes:
- New services: Providing new solutions to a broader scope of customer problems and needs.
- Enhanced services: Improving existing services to enhance performance for the customer.
- Service delivery: Adjusting the company's primary approach to delivering services.
- Customer interaction: Transforming the way a service provider engages and interacts with its customers to enhance customers' value perception, overall experience, and cost-efficiency.
Examples
New services: Monitoring driver behaviour of truck drivers and providing training to truck drivers, nut a truck manufacturer.
Enhanced services: Proactive maintenance to reduce (unplanned) downtime and increase the utilisation rate of the assets.
Service delivery: Remote diagnostics to improve the efficiency of the service activities onsite.
Customer interaction:
- Offer a portal with all information on the status of service requests.
- Conduct quarterly business review meetings.
Service-product-management
As service innovation is all about improving the value for the customer and the company, which involves bringing new services and improving existing services, service innovation and service-product-management closely interrelate.
While interrelated, service innovation and product-service management focus on different aspects of delivering value through services. Understanding their differences and areas of overlap can provide a clearer picture of how they contribute to an organisation's success.
Differences
- Focus and Objective
- Service Innovation:
Concentrates on creating new or improved services that deliver unique value to customers. The aim is to differentiate the business, meet emerging customer needs, or capture new markets through novel service offerings or by enhancing existing services. - Product-Service Management:
Encompasses the ongoing process of managing a service or product-service combination throughout its lifecycle. The focus is ensuring the service remains competitive, meets customer expectations, and aligns with the business strategy.
- Service Innovation:
- Scope
- Service Innovation:
Broad in scope, encompassing the ideation, development, and implementation of new service concepts, processes, or models. It's about change and transformation, pushing the boundaries of what's currently offered. - Product-Service Management:
Concerned with the operational aspects of a service or product-service offering, including development, marketing, delivery, maintenance, and improvement. It's an ongoing process of managing and optimising services.
- Service Innovation:
- Strategic vs. Operational
- Service Innovation
More strategic, focusing on long-term growth opportunities, new markets, and significant enhancements or changes in service delivery. It's about setting new directions and capturing new value propositions. - Product-Service Management
More operational, dealing with the day-to-day management and execution of service strategies. It includes performance monitoring, customer feedback analysis, and incremental service improvements.
- Service Innovation
Overlap
- Customer-Centric Approach
Both service innovation and product-service management prioritise understanding and meeting customer needs. They involve gathering and analysing customer insights to inform service design and delivery. - Continuous Improvement
There's a shared emphasis on continually enhancing service offerings. In service innovation, this might manifest as radical changes or new service introductions, while in product-service management, it often involves iterative improvements and optimisations. - Cross-Functional Collaboration
Successful service innovation and product-service management require collaboration across different organisational functions, including R&D, marketing, sales, and customer service. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that new services are well-designed and effectively managed throughout their lifecycle. - Use of Technology
Both areas increasingly leverage technology to enhance service offerings and delivery. This includes digital platforms, analytics, and emerging technologies like AI and IoT, which can drive innovative new services and the ongoing management and enhancement of existing ones. - Strategic Alignment
Both service innovation and product-service management must align with the broader business strategy. Whether introducing a ground-breaking service or managing existing offerings, the goal is to support the organisation's overall objectives and competitive positioning.
Understanding these differences and overlaps can help organisations strategically integrate service innovation with effective product-service management, ensuring the creation of compelling new services and their successful implementation, management, and continuous improvement.
Why service innovation matters
Significant trends driving service innovation
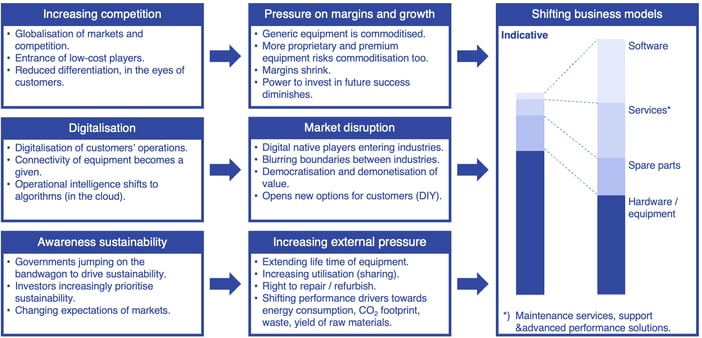
The B2B manufacturing industry is undergoing a significant, challenging, but exciting transformation driven by several key trends:
- Intense Global Competition
Manufacturers worldwide are continually improving, leading to commoditisation and increasing pressure on margins. It's a race to deliver the best, the quickest. - Digital Disruption
The digital revolution is transforming customer expectations and behaviours. Traditional business models are being shaken up, and those who fail to adapt risk becoming obsolete. - Sustainability Imperative
Increasing global awareness of environmental issues presents new opportunities and challenges. Sustainable practices are no longer optional but are becoming a core expectation from customers, investors, and stakeholders.
The stakes are high
With industries rapidly transforming digitally and in services, there's a widening gap between the frontrunners and the laggards.
Laggards experience:
- The risk of overlooking critical opportunities and letting potential growth escape.
- The threat of being overshadowed by competitors.
- Declining trust and confidence from your stakeholders and teams.
- Operations trapped in the outdated mode of business-as-usual, even as the industry moves forward.
- Struggles to attract and retain talents.
- Struggles to attract and retain good investors.
However, the frontrunners are best positioned to experience:
- Accelerated growth.
- Staying ahead of (new) competition.
- Meeting the expectations of your stakeholders.
- Meeting the changing needs of your customers.
- Gaining and sustaining strategic commitment.
- Building confident and engaged teams.
- Attracting the best talents.
- Attracting the best investors.
The bottom line: Enriching business models with innovative services and software is becoming a critical factor for success for B2B manufacturers. The service transformation is not just a strategic option—it's a vital move for the survival and growth of your business.
Develop a strategic approach
Service innovation is essential for driving sustainable service transformation and growing the service business. It must be propelled by a coherent winning service strategy that articulates growth drivers.
Align with a Winning Service Strategy
Aligning service innovation with a winning service strategy establishes a cohesive direction for innovation efforts. It ensures alignment with organisational goals, fostering clarity and purpose in service development.
Articulating clear objectives and strategic priorities guides decision-making and inspires teams towards shared goals, driving impactful outcomes and sustainable growth.
Understand Business Domain Evolution
It's vital to develop the domain expertise of your customers' businesses and how they manage and optimise their operations and assets.
By thoroughly understanding their developmental path, you can better anticipate their (emerging) needs and challenges. This comprehensive insight allows us to tailor your service offerings more precisely, ensuring they are relevant and instrumental in supporting your customers' growth and operational advancements.
Define Strategic Differentiation
Strategic differentiation is the cornerstone of a successful service strategy. It involves articulating how the service provider will add unique value and stand out from competitors.
To avoid the commoditisation trap, businesses must offer distinctive solutions and experiences that set them apart from competitors and new entrants. This may involve leveraging unique capabilities, delivering unparalleled customer experiences, or offering innovative solutions that address unmet customer needs.
By defining clear points of differentiation, businesses can carve out a unique position in the market and establish a competitive advantage that is difficult for rivals to replicate.
Identify Core Capabilities
Developing core capabilities is a crucial component of a winning service strategy and, therefore, integral to service innovation.
These core capabilities form the bedrock upon which the strategy is built and operationalised. To equip the business for strategic success, it's imperative to thoroughly assess existing capabilities and pinpoint areas needing development or enhancement in alignment with strategic ambitions.
Articulate Growth Drivers
While innovation is often equated with advancement, its impact on revenue growth isn't always straightforward. Enhancing services with advanced features doesn't necessarily guarantee growth, especially when these enhancements have become commoditised across the industry or are merely seen as expected periodic improvements. This nuance underscores the importance of discerning between innovations that merely sustain operations and those that can truly catalyse revenue growth.
Understanding the Drivers of Growth
Identifying the real levers of growth is crucial. This involves recognising strategies that can effectively capture market share, bolster pricing power, broaden the addressable market, venture into new territories, and increase the portion of the customer's wallet captured. These drivers go beyond incremental service improvements, focusing on creating distinct value that sets a business apart in the competitive landscape.
Defining Growth Objectives
Setting ambitious and clear growth objectives is vital in service innovation. These goals should be aligned with the broader service strategy, propelling the organisation toward its envisioned future. Establishing tangible growth targets, whether related to market penetration, revenue increments, or enhanced customer loyalty, focuses on the organisation's endeavours. It channels resources toward high-impact initiatives capable of delivering meaningful and lasting growth, navigating beyond commoditised service enhancements to uncover genuine opportunities for expansion.
Define Innovation Tracks
By outlining innovation tracks, organisations establish a structured framework for identifying and pursuing strategic opportunities in service innovation and differentiation.
Identifying Strategic Innovation Opportunities
Describing the innovation tracks that closely align with the organisation's service strategy and overarching objectives.
These tracks should cater to various strategic goals, including growth, efficiency, performance enhancement, and elevating customer experience.
By carefully considering emerging market trends, evolving customer preferences, and technological advancements, organisations can ensure that their innovation tracks are purposeful and directed towards driving tangible outcomes that contribute to long-term success.
Define a Mission Statement for Each Innovation Track
Clearly define the mission and purpose of each track. This should be concrete and open for creativity and exploration at the same time.
By providing a clear direction for each innovation track, organisations can streamline decision-making processes, allocate resources effectively, and drive meaningful results that foster sustainable growth and success.
An example could be: Drive operational efficiencies for your customers with smart technology.
Establish a Service Roadmap
A well-defined service roadmap provides clarity of priorities over time, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives.
It offers focused inspiration in each phase, guiding decision-making with clear objectives and milestones.
This structured approach fosters agility and adaptability, essential for navigating dynamic market conditions and driving sustainable growth.
Setting Strategic Objectives
Setting strategic objectives forms the cornerstone of establishing a service roadmap. These objectives should be clear, measurable, and aligned with the organisation's overarching winning strategy.
In addition to overarching goals, strategic objectives within the service roadmap should encompass the development of new value propositions, service offerings, and service capabilities.
This proactive approach ensures that the organisation continuously innovates and evolves its service portfolio to meet customers' changing needs and preferences and capitalise on emerging market opportunities.
Creating a Time Window
A crucial aspect of establishing a service roadmap is defining a realistic and achievable time window for accomplishing strategic objectives. This involves striking a balance between short-term milestones and long-term goals, allowing for steady progress while also maintaining a focus on the organisation's broader vision.
By establishing a clear timeframe for achieving strategic objectives, the organisation can effectively prioritise initiatives, allocate resources, and monitor progress towards its desired outcomes. This time-bound approach provides a sense of urgency and accountability, driving momentum and ensuring that efforts remain aligned with overarching strategic priorities.
Adapting to Change
Recognising the business environment's dynamic nature, embedding flexibility into the service roadmap is imperative to accommodate changes and uncertainties.
Market conditions, customer needs, and internal capabilities constantly evolve, requiring the organisation to remain agile and responsive. Building flexibility into the roadmap allows the organisation to pivot quickly in response to emerging opportunities or challenges, ensuring that strategic objectives remain relevant and achievable.
This may involve periodic reviews and adjustments to the roadmap and a willingness to experiment and iterate based on real-time feedback and insights. By embracing change and adaptability, the organisation can position itself for sustained success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Read more strategy approach of service innovation:
Drive Faster Service Transformation with Your Innovation Strategy
Drive a balanced portfolio of initiatives
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, innovation catalyses growth and adaptation.
However, organisations often fall into the trap of prioritising short-term gains or merely focusing on the usual suspects all competitors are pursuing as well.
To navigate successfully through changing market dynamics and ensure long-term sustainability, it is essential to cultivate a balanced portfolio of initiatives.
Why This Matters
Balancing initiatives within an organisation's innovation portfolio is crucial to avoid bias towards a single type of innovation, which can lead to:
- Missed growth opportunities for the short-term.
- Missed opportunities for long-term growth and innovation.
- Inability to respond more effectively to market changes, customer needs, and emerging trends.
Frameworks for Differentiating Types of Innovation
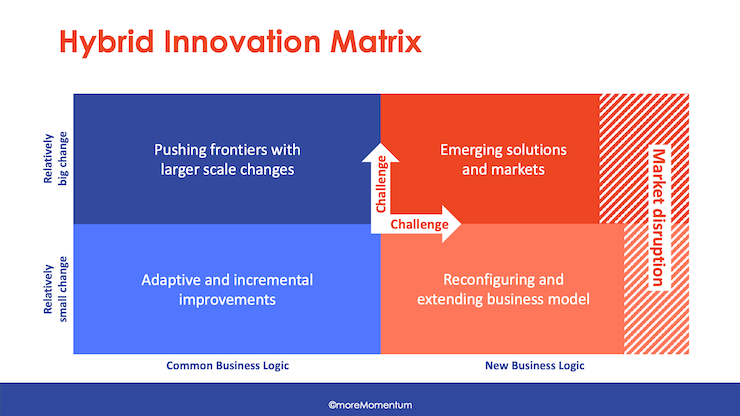
Hybrid Innovation Matrix
This framework describes the relative magnitude of innovations and whether they involve existing or new business logic. It categorises innovations into quadrants such as Incremental Improvement, Pushing the Frontiers, Reconfiguring the Business Model, and Emerging Markets of New Solutions to New Problems.
Read more the Hybrid Innovation Matrix:
How to Organise for Servitization
Sustaining Innovation vs. Innovation for Growth
Distinguishing between sustaining innovations, which maintain existing operations, and innovations for growth, which drive transformation and expansion.
21 Tracks of Innovation
A comprehensive framework that categorises innovation initiatives into Value Proposition, Value Delivery, and Value Capture tracks, providing a structured approach for understanding and prioritising innovation efforts.

Read more about the innovation tracks:
Diversify your service innovation to boost growth
3 Box Approach
Segment initiatives into three categories based on time horizons: Today (incremental improvements), Tomorrow (value proposition development, business model reconfiguration), and the Day After Tomorrow (anticipating emerging solutions for emerging problems).
This approach can be easily combined with the Hybrid Innovation Matrix by designating a time window for each quadrant.
Practical Implementation
- Define Tracks in Different Buckets
Categorise innovation initiatives into distinct buckets based on their strategic focus and objectives, ensuring clarity and alignment with organisational priorities. - Resource Allocation
Allocate resources per bucket, prioritising initiatives within each category based on their strategic importance and potential impact. This approach ensures that resources are effectively allocated and initiatives adequately funded to drive desired outcomes.
Example Resource Allocation
- Allocate 3% of service revenue for service innovation, reflecting a commitment to driving continuous improvement and innovation in service offerings.
- Distribute 60% of the innovation budget for short-term initiatives, focusing on incremental improvements and optimising existing processes and services.
- Allocate 30% of the budget for mid-term initiatives, which involve developing new value propositions and reconfiguring business models to drive growth and differentiation.
- Allocate 10% of the budget for longer-term initiatives, focusing on anticipating emerging solutions for emerging problems, ensuring that the organisation remains agile and future-ready in a rapidly changing landscape.
Follow the phases
Understanding the distinct phases of service innovation is essential for service providers to effectively navigate the challenges and capitalise on the opportunities inherent in the innovation process. Each stage represents a critical milestone, offering unique insights and guiding actions to drive innovation success. This comprehensive outline delves into the various phases of service innovation, highlighting the tactics and techniques required to excel at each stage.
Why This Matters
Recognising the significance of following a phased approach to service innovation is paramount, as it helps avoid the common mistake of prematurely advancing to later stages without adequate groundwork.
Many organisations fail to apply appropriate techniques and best practices at each phase, leading to challenges in convincing customers of the value proposition and securing their willingness to pay.
Symptoms of this oversight often manifest as questions like:
- How can we convince our customers about the value and get them to pay?
- We struggle to differentiate our service from competitors and articulate its unique value proposition.
- Our customers seem hesitant to adopt our new service, and we're unsure how to address their concerns.
By understanding the importance of each stage and employing the right tactics at the right time, organisations can mitigate risks, optimise resource utilisation, and enhance the likelihood of innovation success.
Download your Free Guide to Your Service Innovation
Phase 1: Generating and Developing Ideas
Understanding the Phase
In the initial phase of service innovation, the focus is on generating and developing ideas that address identified market gaps and cater to unmet customer needs. This stage is the foundation for the entire innovation process, setting the direction and scope for subsequent activities.
Engaging in Brainstorming and Research
Based on these strategic insights, the following tactics will be the core of generating innovative ideas:
- Brainstorming Sessions
Organising collaborative brainstorming sessions allows teams to pool diverse perspectives and insights, fostering creativity and idea generation. - Market Research
Conducting thorough market research helps identify emerging trends, understand competitor offerings, and uncover latent customer needs. - User Discussions
Engaging in discussions with potential users provides valuable feedback and insights, ensuring that ideas are aligned with real-world requirements and preferences.
Utilising Innovative Techniques
However, to ensure you do not get stuck into the obvious ideas, at the tip of the iceberg, more advanced techniques are required, like:
- Empathic Design
Empathic design techniques involve putting oneself in the customer's shoes to gain deep insights into their experiences, preferences, and pain points. - Design Thinking
Applying design thinking principles encourages a human-centred approach to problem-solving, emphasising empathy, creativity, and iterative prototyping. - Observations
Observational research techniques involve directly observing user behaviours and interactions with existing products or services, uncovering valuable insights for idea generation.
Challenges
Common challenges companies face in this stage are:
- Lack of Customer Insights
Without a deep understanding of customer needs, preferences, and pain points, ideation efforts may lack relevance and fail to address genuine market gaps. - Strategic Alignment
Strategic objectives and market positioning should guide ideation to ensure that ideas align with the organisation's goals and contribute to differentiation and growth. - Lack of Direction
Without clear guidance or direction, teams may struggle to focus their ideation efforts, leading to a proliferation of ideas that lack coherence or strategic relevance. - Stuck in Common Thinking
Ideation efforts may fall short of generating truly innovative ideas if teams are constrained by conventional thinking or are overly influenced by existing industry practices. This can result in ideas that fail to differentiate the organisation from competitors or drive meaningful growth.
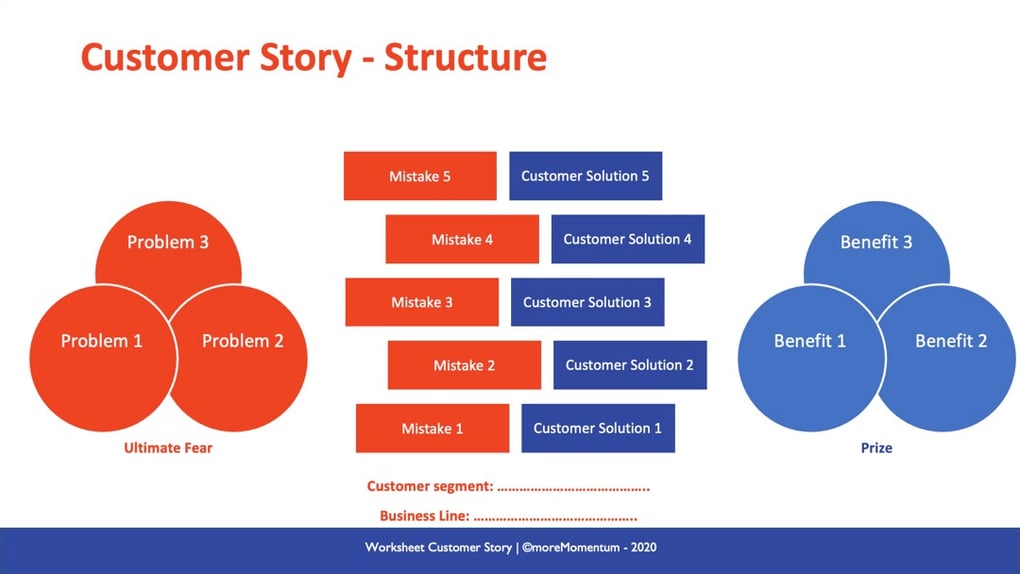
Read more about Customer Insights:
Build A Strong Customer Story In 7 Steps To Build Irresistible Services
Phase 2: Developing the Service
In the second phase of service innovation, the focus shifts from ideation to the actual development of the service offering. This phase involves translating conceptual ideas into tangible solutions, refining them based on feedback, and laying the groundwork for successful implementation.
Establishing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
A critical aspect of service development is the creation of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), which serves as an initial version of the service introduced to a select group of users. The MVP allows organisations to test critical hypotheses and gather early feedback on aspects such as customer problem-solution fit, willingness to pay, and feasibility of delivery.
This iterative process often begins with simple prototypes, such as slide decks or mock-ups, and evolves through successive iterations based on user feedback.
The goal is to validate assumptions, make necessary adjustments, and ultimately refine the service to meet customer needs better.
Read more about experiments:
Reduce Risks of Service Innovation by Experiments
Focus on Core Features
During service development, it's essential to focus on core features that encapsulate the essence of the service and differentiate it from competitors.
By prioritising these features, organisations can ensure that resources are allocated effectively and that the service delivers maximum value to customers. Engaging with initial users is crucial during this phase to validate problem-solution fit and gauge their willingness to pay for the proposed solution.
Projections or Business Case
In parallel with service development, organisations may also conduct projections or develop a business case to evaluate the proposed service's financial viability and potential return on investment. This involves forecasting revenue streams, estimating costs, and assessing the overall business impact of the service initiative.
While projections provide valuable insights into the potential financial outcomes, it's essential to recognise that they are based on assumptions and should be regularly revisited and adjusted as the service evolves.
Common Challenges and Mistakes
Despite the importance of thorough testing and validation, organisations often encounter challenges and make mistakes during the service development phase. These may include:
- Not Thoroughly Testing
Failure to adequately validate (or falsify) critical assumptions about customer needs, solution feasibility, and willingness to pay can result in misalignment between the service offering and market demand. - No Early Adjustments, Pivots, or Termination of Ideas
Failing to make early adjustments or pivot in response to feedback can lead to costly failures and erode confidence in the innovation process. It's essential to be agile and responsive, willing to iterate or pivot as needed to improve the service offering. - Not Developing All Aspects of Value Proposition
Neglecting to develop all aspects of the value proposition, including the delivery model and capabilities, can limit the effectiveness and appeal of the service. It's crucial to consider the holistic value proposition and ensure that all elements are adequately developed to deliver a compelling customer experience.
Read more about developing a complete solution for customers:
Accelerating Your Customers' Adoption of Your Advanced Services
Phase 3: New Service Introduction
As the service undergoes refinement and gains confidence in its market fit, the focus shifts towards its official introduction to the market. This phase involves internal preparations to ensure organisational readiness and external efforts to attract and onboard new users.
Internal Preparations
Internally, organisations must build the necessary capabilities, capacity, and resources to support the successful launch of the new service. This includes enhancing technical capabilities and developing commercial competencies to facilitate sales and customer support.
Transitioning from a development-centric focus to a customer-facing approach is critical during this stage, with a shift towards empowering sales teams and reducing dependency on the development team for support.
External Rollout
Externally, a comprehensive marketing strategy is essential to drive awareness and adoption of the new service. This involves launching targeted campaigns to reach potential customers and strategically onboard new users. Identifying the right customer segments and assessing their specific needs and maturity levels is crucial for tailoring marketing efforts and ensuring a successful market entry.
Engaging with early adopters and soliciting customer feedback is vital during this phase to validate product-solution fit, assess delivery experiences, and promptly address any issues or omissions.
Agile Development and Continuous Feedback
Adopting agile development methodologies, such as sprint cycles and continuous feedback loops, is instrumental in facilitating the successful introduction of new services. By iterating quickly and incorporating feedback from users, organisations can adapt and refine the service in real-time, ensuring that it meets evolving market demands and customer expectations.
Challenges
- Scaling Before Product-Market Fit
One common challenge is the temptation to scale operations prematurely before achieving product-market fit and validating the service's viability in the market. Rushing into scaling without adequate feedback can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities for refinement. - Targeting the Wrong Market Segment
Another challenge is the risk of misidentifying or inadequately targeting the right customer or market segment. Failing to align the service with the needs and preferences of the target audience can result in poor adoption rates and limited market penetration. - Underdeveloped Sales Capability
Not sufficiently developing sales capabilities, enablement, and collateral can hinder the successful introduction of new services. Without adequate sales support and resources, organisations may struggle to effectively communicate the service's value proposition and convert leads into customers.
Read more about New Service Introduction
Mastering New Service Introduction: The Often-Overlooked Key To Success
Phase 4: Establishing Product-Market Fit
In this phase, the focus shifts to gauging the broader market's response to the service and validating its widespread appeal. As the service gains traction and matures, organisations aim to establish product-market fit, where demand is easily generated and the offering resonates with a larger audience.
Engagement with a Larger Audience
Central to this phase is engaging with a broader audience to gather data on adoption rates and assess market response. Organisations cast a wider net, reaching out to potential customers across different segments to gather insights and feedback.
By soliciting input from a diverse audience, organisations can gain a more comprehensive understanding of market needs and preferences, informing refinements to the service offering.
Refinement Based on Market Feedback
Based on the feedback gathered from the broader market, organisations refine the service offering to better align with market demand. This may involve iterating on features, adjusting pricing strategies, or enhancing the overall customer experience.
The goal is to fine-tune the service to maximise its appeal and effectively address market needs and preferences.
Indicators of Product-Market Fit
Key indicators of product-market fit include a clear value proposition, a well-defined target market, consistently growing demand, positive customer feedback and the ability of the sales teams to sell the service without support from the development teams.
Organisations track metrics such as growth rate and conversion rate to assess the service's performance and its alignment with market demand. As these metrics trend upwards, organisations gain confidence in the service's market fit and its potential for scalability and growth.
Challenges and Mistakes
- Failure to Adjust Commercial Model and Messaging
One common challenge organisations face in this phase is the failure to adapt their commercial model, messaging, and offering to cater to a larger base of customers, particularly the early majority. Failing to tailor commercial strategies and messaging to resonate with this broader audience can result in missed market penetration and growth opportunities. Organisations must ensure that their commercial approach aligns with the evolving needs and preferences of the expanding customer base. - Underdeveloped Commercial Capabilities
Another challenge is the risk of relying too heavily on development teams for commercial support and resources. Organisations must invest in developing robust commercial capabilities, including sales, marketing, and customer support functions, to operate independently from development teams. Failing to develop these capabilities can lead to inefficiencies, delays, and missed opportunities for scaling and growth. Organisations need to build a solid commercial infrastructure that can effectively support the service's expansion and drive sustainable growth in the market.
Phase 5. Scaling and Maturing
This phase emphasises expanding the service's reach and continuously enhancing its capabilities to accommodate growth and evolving market demands. As the service gains traction, organisations explore new market segments, gather ongoing feedback, and iterate on improvements to ensure ongoing relevance and competitiveness.
Expanding Reach and Improving Capabilities
With initial traction established, organisations shift their focus towards scaling the service and maturing its capabilities. This involves exploring opportunities to penetrate new market segments, catering to a broader customer base, and extending the service's reach. Concurrently, organisations prioritise continuous improvement efforts to enhance the service's functionality, performance, and user experience.
Agile Approach and Adaptability
Embracing agility, rapid iterations, and adaptability principles is essential for managing growth effectively during this phase. Organisations leverage agile methodologies to iterate quickly on enhancements and adjustments, ensuring the service remains aligned with evolving market needs and competitive dynamics. By staying nimble and responsive, organisations can navigate challenges and capitalise on opportunities for growth.
Standardisation for Efficiency and Margin Improvement
As the service scales and matures, organisations focus on standardising processes to drive efficiency and margin improvement. This involves streamlining operations, optimising resource allocation, and implementing best practices to enhance cost-effectiveness and profitability. By standardising processes, organisations can achieve greater scalability and sustainability while maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Common Challenges and Mistakes
- Failure to Develop for Mass Market
One common challenge organisations encounter is the failure to adapt the service to cater to a larger mass market. Focusing exclusively on niche segments or failing to scale the service for broader adoption can limit growth opportunities and hinder market penetration. - Lack of Cost-Effectiveness
Another challenge is the risk of neglecting cost-effectiveness in pursuit of growth. Organisations must balance expansion efforts with cost management strategies to ensure sustainable growth and profitability. Ignoring cost-effectiveness can lead to financial strain and undermine long-term viability. - Feature-Driven Development Over Strategic Competitiveness
Falling into the trap of feature-driven development, focusing on adding superficial enhancements rather than strategicallycompetitive features, is a common mistake. Organisations must prioritise investments that deliver tangible value to customers and enhance the service's competitive positioning in the market.
Read more about methodologies for the different phases:
Tailoring the Right Innovation Methodology for Each Phase in B2B Services
Put customers at the center
In every phase of service innovation, deep customer insights are essential. Customers are primarily interested in solving problems, pursuing opportunities, and improving their lives. Therefore, it's crucial to centre all service innovation efforts around addressing their needs and preferences.
Types of customer needs
Roughly, customer needs can be categorised into the following:
Relieving Customers from Unwanted Activities
Customers often look to be liberated from tasks that divert their focus from their primary business activities. They seek solutions that can handle peripheral duties such as maintenance, regulatory compliance, and administrative work, enabling them to concentrate on their primary business goals and enhance their operational efficiency.
Enabling Customers to Perform Essential Activities
Customers need tools and solutions that empower them to execute their activities more effectively and/or efficiently. They require access to cutting-edge technology, expertise, and support to elevate operational standards, facilitating innovation and ensuring their competitive edge in the market.
Making Customer Activities Easier
In an environment marked by complexity, customers strongly desire solutions that make their daily operations more manageable. They look for innovations that streamline processes, offer intuitive interfaces, and provide responsive customer support, thus reducing the time and effort needed for routine tasks and allowing them to allocate resources more strategically.
Delivering Complete Solutions
Customers are in search of complete solutions that not only meet their immediate needs but seamlessly integrate into their existing ecosystems. They value tailored services that consider the full scope of their operational challenges, including adoption barriers. They deliver a comprehensive package that includes customised products, thorough training, and continuous support, facilitating a smooth adoption process and long-term value.
Linking Attributes to Benefits and Values
Customer Value = Total Customer Benefits - Total Customer Costs
Aligning product attributes with the benefits customers seek allows you to develop offerings that deeply connect with their audience, delivering high value.
When services and products are designed to directly address customers' strategic goals, operational efficiencies, and broader challenges, they become integral to the customer's success. This is key to crafting value propositions that satisfy and delight customers, fostering loyalty and driving growth.
Understanding customer value requires a comprehensive view of all benefits and costs involved.
The costs go beyond just the price of the service. This includes the risks, adjustments in work processes, and any potential disruptions that come with adopting new solutions.
Advance your service innovation and service-product-management capabilities
One of the most significant challenges is the service innovation and service-product-management capabilities and capacity within product-centred companies. This gap hinders their ability to drive an adequate pace in their service transformation and to grow their service business.
Developing Capacity for Service Innovation and Service-Product-Management
The foundation of service innovation lies in developing the required capacity. This involves allocating resources strategically to support service innovation initiatives. Manufacturing firms need to invest in dedicated teams, technological infrastructure, and innovation labs that can pilot new service concepts.
Creating a cross-functional team that draws from various departments, such as R&D, marketing, operations, and customer service, can provide diverse perspectives and foster a culture of innovation.
Organising the Service Innovation and Service-Product-Management Functions and Its Governance
To effectively drive service innovation, it's crucial to establish a clear organisational structure and governance model.
This structure should define the roles and responsibilities of the service innovation team, ensuring they have the autonomy and authority to make strategic decisions.
The governance model should outline idea generation, evaluation, development, and implementation processes, ensuring service innovation aligns with the overall business strategy. This organisational clarity helps prioritise projects, manage resources efficiently, and scale successful innovations across the firm.
Developing Skills and Capabilities
For service innovation and service-product-management to flourish, manufacturing firms must focus on developing the required skills and capabilities within their teams.
This includes training in design thinking, customer experience management, digital technologies, and data analytics.
Encouraging a mindset shift from a product-centric to a service-dominant mindset is vital. Employees should be empowered to think about the entire lifecycle of customer engagement, focusing on creating value through services. Collaborating with external partners, academic institutions, and industry consortia can also bring fresh insights and expertise to accelerate the development of these capabilities.
Differentiate for the different types of innovation
The innovation landscape is diverse, with every kind of innovation—incremental, disruptive, radical, or architectural—bringing its own characteristics, challenges, and rewards.
The uncertainty and unpredictability are typically higher in disruptive and radical innovations, where customer preferences, competitor responses, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes can shift dramatically and without clear precedent.
These types of innovations often face a higher risk of failure due to their ground-breaking nature. Still, the potential benefits of success can be game-changing, offering significant competitive advantages and market leadership opportunities. Conversely, incremental and architectural innovations, while still requiring creativity, tend to operate within a more predictable and familiar framework, making the associated risks and uncertainties somewhat lower.
Given these varied landscapes, each type of innovation demands distinct approaches:
- Ideation Methods
Radical and disruptive innovations may benefit from open innovation platforms, hackathons, or blue-sky thinking sessions encouraging boundary-pushing ideas. In contrast, incremental and architectural innovations might rely more on customer feedback loops and continuous improvement methodologies. - Development Methods
High-risk innovations might necessitate agile, experimental approaches with rapid prototyping and testing to navigate uncertainties. More predictable innovation types could follow structured development processes with clear stages and milestones. - Decision-Making for Go/No-Go
Disruptive or radical innovations require a tolerance for ambiguity and a willingness to bet on less certain outcomes, possibly leveraging venture capital models for decision-making. Incremental innovations can often use data-driven decision-making with more explicit ROI calculations. - Resource Allocation
Pioneering innovations often need flexible, risk-tolerant funding, akin to venture capital, with the understanding that investments are high-stakes. Given their more predictable returns, incremental innovations might be funded through traditional budgeting processes. - Required Skills
The disruptive innovation team might need individuals who are comfortable with ambiguity and have skills in emerging technologies and markets. Incremental innovation teams might require deep industry knowledge and expertise in continuous improvement processes. - Delegation of Decisions
Radical innovations may benefit from decentralised, empowered teams that can make quick decisions on the ground, while incremental innovations might follow more traditional, hierarchical decision-making paths. - Development Team Proximity
Teams working on ground-breaking innovations may need to operate semi-autonomously, perhaps as a "skunkworks" group distanced from the core business to foster creative freedom. Teams focused on incremental improvements may be more integrated within the business units to ensure alignment with ongoing operations.
Each innovation type's unique demands underscore the need for tailored management, development, and cultural strategies to harness its potential and navigate its challenges effectively.
Measuring success and impact
Measuring success and the impact of new initiatives is crucial for strategic growth and continuous improvement in the dynamic landscape of service innovation within manufacturing. This requires a balanced set of metrics to monitor the success of their service innovation.
Metrics of Business Outcomes
The ultimate goal of service innovation is to drive positive business outcomes. Key metrics in this area include:
- Growth
This can be measured in revenue growth attributable to new service offerings, indicating the direct financial impact of innovation efforts. - Adoption
The rate at which customers adopt new services reflects their market acceptance and relevance. High adoption rates are often indicative of well-designed services that meet customer needs. - Loyalty
Customer retention rates and repeat business are critical for assessing how service innovations contribute to building and maintaining strong customer relationships. - Share of Wallet
An increase in the share of wallet, or the proportion of a customer's total spending captured by the firm, signifies the ability of service innovations to enhance customer value and cross-sell effectively. - Service Quality and Performance Metrics
Include service reliability, responsiveness, and consistency measures, which are key indicators of operational excellence in service delivery. Regularly tracking these metrics can help ensure your service innovations maintain high standards throughout their lifecycle. - Efficiency and Productivity
Assess the operational efficiency of your service delivery, including the utilisation of resources and the productivity of service operations. This can highlight areas for optimisation and improvement in managing your service offerings. - Cost-to-Serve
Analyse the cost implications of your service innovations, not just in initial development and launch but also in ongoing delivery. Understanding and managing the cost-to-serve is crucial for ensuring the financial sustainability of your service offerings. - Service Satisfaction Scores
Beyond initial adoption, measure customer satisfaction with your services' quality, reliability, and overall experience. This can provide insights into the effectiveness of your service-product management practices in maintaining high customer service standards. - ROI of Innovation Initiatives
Calculate the return on investment for your service innovation initiatives, considering both the direct financial returns and the intangible benefits, such as enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Metrics about learning
Innovation is as much about learning as it is about outcomes. Important metrics include:
- Feedback on New Offerings
Qualitative and quantitative feedback from customers on new services provides insights into market fit, potential improvements, and unmet needs. - Adaptation of Business Models
The degree to which new business models are embraced internally and externally can reveal flexibility and responsiveness to market changes. - Understanding Evolving Customer Needs
Regularly assessing how well new services align with and anticipate customer needs is vital for ensuring long-term relevance and competitiveness. - Customer Feedback Loops
Implement systematic processes for collecting and analysing customer feedback on your services. This can inform continuous improvement efforts and help align your service innovations more closely with customer needs and expectations.
Metrics about the progress of Initiatives
Measuring the progress of service innovation initiatives ensures that projects stay on track and resources are used efficiently. Key considerations include:
- Milestone Achievement
Tracking progress against predefined milestones helps assess the pace and direction of innovation projects. - Resource Allocation
Monitoring how resources are allocated and utilised across different innovation initiatives can highlight areas of efficiency and potential waste. - Adaptability
The ability to pivot or iterate on service offerings in response to feedback and changing market conditions is crucial for sustaining innovation momentum. - Time-to-Market and Time-to-Volume
Measure the efficiency of bringing new services from concept to market and then to the desired scale. This reflects the operational effectiveness and agility of your service-product management processes. - Portfolio Balance and Health
Assess the balance and health of your service portfolio, considering factors such as service maturity, market demand, and revenue contribution. This can inform strategic decisions about where to invest, where to divest, and where to innovate within your service offerings.
How moreMomentum can contribute
moreMomentum is a global service community that inspires and facilitates service leadership and development teams in B2B manufacturing to drive a winning pace in their service transformation.
They are navigating exciting, but complex service transformations, with major developments in their service strategy, service development, revenue generation, service operations and much more.
Our community meetings, Service Transformation Monitor, Service Academy and Advisory Services support service leadership and development teams to stay current, develop their teams, boost their service initiatives with a competitive.

Service innovation is one of the pillars we cover :
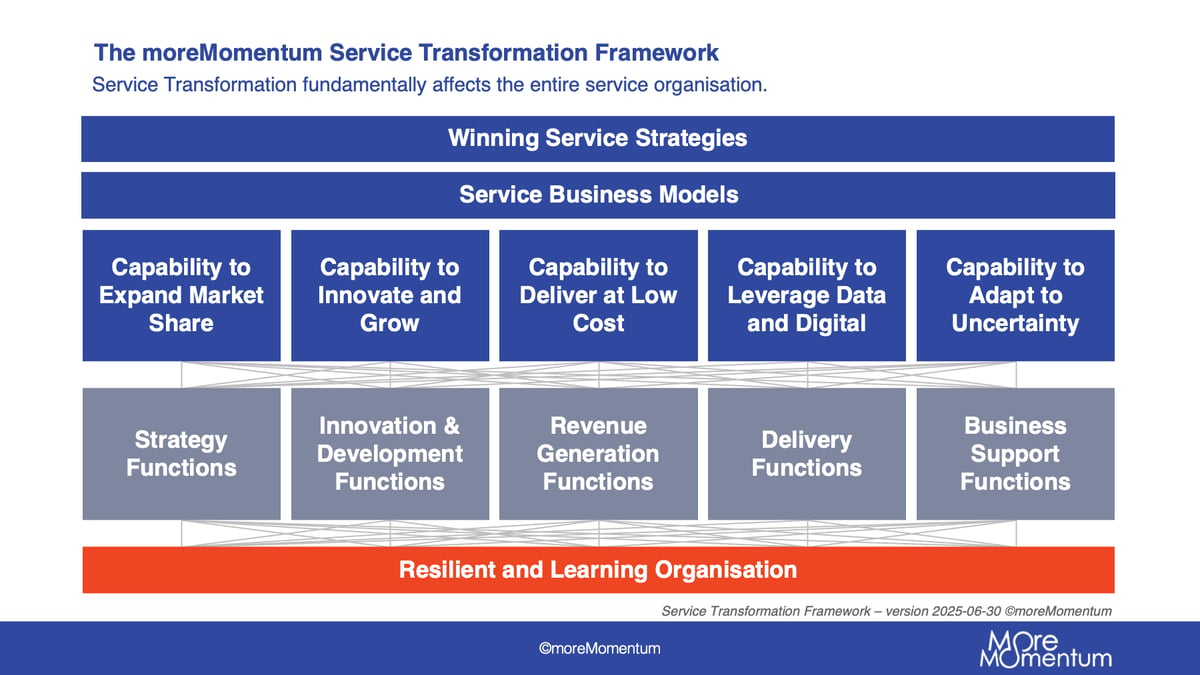
For our members and customers, we offer the following services: