Your Ultimate Guide to Your Service Transformation
Build and maintain your pace in your service transformation.
Free Download
The Complete Guide
Everything you need to accelerate and maintain your pace in your service transformation.
Download now and read later

In today's dynamic business environment, service transformation is more than just a buzzword; it's a complex, multifaceted journey that reshapes how organisations deliver value to their customers. As industries evolve and customer expectations rise, companies face the challenge of reinventing their service offerings to stay relevant and competitive.
Navigating this intricate landscape requires a clear roadmap and strategic direction. The Service Transformation Framework offers a comprehensive guide that demystifies the complexities, providing businesses with actionable insights and tools to accelerate their transformation efforts, ensuring sustained success in an ever-changing market.
Keep reading or use the chapter links below to jump ahead.
-
In this guide
- What is service transformation
- Examples of service transformation
- Why is service transformation important
- Service Transformation Framework
- Service Transformation process
- The need for a high pace
- How to increase and maintain your pace
- The Pivotal Role of Leadership and Innovation Teams
- Conclusion - The Imperative of a high pace
What is service transformation?
Service transformation is the process of evolving how a company delivers value to its customers through services.
It involves three fundamental changes:
- Service Operations: Improving how services are provided, ensuring they are efficient and meet customer needs.
- Service Business Model: Developing new service offerings and models, aligning them with changing market demands.
- Overall Business Model: Adjusting the company's primary approach to delivering value with services, data, software, and products, ensuring it remains relevant and competitive.
Examples of service transformation
Service Operations
Predictive maintenance - A proactive approach to service operations
Background
Traditional maintenance services in the industrial machinery sector often operate on a reactive basis. A technician is dispatched to address the issue when a machine breaks down. While this approach has been standard for years, it frequently results in extended downtimes, unexpected production interruptions, and increased operational costs.
The Predictive Maintenance Approach
Implementing predictive maintenance becomes essential to transition from a reactive to a proactive service model. This approach integrates sensors and IoT devices into machinery, continuously monitoring equipment health and performance. Advanced algorithms then analyse the collected data, predicting potential failures before they manifest.
Benefits
Adopting predictive maintenance offers several advantages:
- Minimised Downtimes
Identifying potential issues early can address disruptions before they escalate into significant breakdowns. - Cost Efficiency
Preventing breakdowns translates to reduced repair costs and avoids the financial implications of halted production. - Elevated Customer Satisfaction
With fewer disruptions, customers experience a smoother operation, increasing trust in the service provider. - Data-Driven Decision Making
Continuous data collection offers insights into machine performance patterns, enabling better design, manufacturing, and optimisation strategies in the future.
Conclusion
The predictive maintenance approach transforms service operations from merely addressing issues to anticipating and preventing them. Doing so offers a more efficient, cost-effective, and customer-centric service model, setting the stage for industry leadership in the modern manufacturing landscape.
Remote diagnostics - A modern approach to service operations
Background
Historically, when equipment or machinery faced issues, the immediate response was to send a technician on-site to diagnose the problem. This method, while effective, often resulted in delays, increased costs due to travel and logistics, and prolonged downtimes, especially if the equipment was located in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
The Remote Diagnostics Approach
To streamline and enhance the diagnostic process, remote diagnostics emerges as a game-changer. Leveraging advanced sensors, IoT devices, and real-time data transmission, issues with machinery can be diagnosed remotely by experts worldwide. This approach allows for immediate analysis without the need for physical presence.
Benefits
Implementing remote diagnostics brings forth several advantages:
- Rapid Response
Diagnostics can be initiated when an issue arises, reducing the time to identify and address problems. - Cost Reduction
Travel and logistics expenses are significantly saved by avoiding technicians travelling to the site for initial diagnostics. - Enhanced Efficiency
Experts can handle multiple diagnostic sessions simultaneously, leading to better resource utilisation. - Data Collection and Analysis
Continuous monitoring and diagnostics provide a wealth of data, offering insights into common issues, performance metrics, and areas for improvement.
Conclusion
The remote diagnostics approach revolutionises service operations by offering a more responsive, efficient, and cost-effective solution. Diagnosing issues in real-time from any location ensures that equipment downtimes are minimised, and operations remain smooth, positioning service providers at the forefront of modern service solutions.
Service Business Model
Supported self-service - A progressive approach to service business models
Background
Traditionally, when customers encountered issues or needed assistance with a product or service, they would rely entirely on the service provider's team for solutions. This often meant waiting for available support, leading to potential delays and sometimes dissatisfaction, especially during peak times or for minor issues that could be resolved quickly.
The Supported Self-Service Approach
In a transformative shift, the supported self-service model empowers customers to address and resolve their issues independently. This approach provides customers with comprehensive resources, tools, and training, enabling them to handle various tasks or troubleshoot problems on their own. However, if they encounter challenges or need further assistance, expert support remains readily available to guide them.
Benefits
Adopting a supported self-service model offers several key advantages:
- Empowered Customers
Equipping customers with the necessary knowledge and tools allows them to resolve issues faster and conveniently. - Reduced Support Overhead
With customers handling many minor issues themselves, the service team can focus on more complex or specialised requests, optimising resource allocation. - Scalability
As the customer base grows, the model scales effectively without needing proportional increases in support staff. - Continuous Learning
Offering training modules, tutorials, and knowledge bases ensures that customers have up-to-date information, enhancing their proficiency and confidence in using the product or service.
Conclusion
The supported self-service approach redefines the service business model by balancing customer independence and expert support. By empowering customers and providing them with the necessary training and resources, service providers can enhance customer satisfaction, reduce operational costs, and foster a proactive service culture, setting a new standard in customer-centric service delivery.
Outcome-based services - Delivering tangible business results
Background
In the traditional service paradigm, providers often focus on delivering specific tasks or functions, such as equipment maintenance or software updates. While these services met immediate needs, they didn't necessarily align with the broader business goals of the customer, such as improving operational efficiency or reducing costs.
The Outcome-Based Services Approach
Pivoting from task-oriented to results-driven, outcome-based services are designed to achieve specific business outcomes for the customer. Providers commit to delivering tangible results instead of just providing a service, such as reducing energy consumption, enhancing raw materials yield, or boosting operations' overall efficiency. This approach fosters a deeper partnership between service providers and customers, with both parties invested in achieving the desired outcomes.
Benefits
Transitioning to an outcome-based service model offers a host of advantages:
- Aligned Objectives
Service providers and customers work collaboratively, ensuring services are tailored to achieve specific business goals. - Value Creation
By focusing on outcomes, providers deliver services that directly impact the customer's bottom line, creating tangible value. - Risk Sharing
Both parties share the risks and rewards, fostering trust and long-term partnerships. - Data-Driven Decisions
Continuous monitoring and feedback loops ensure that services are optimised based on real-world performance data, leading to better results over time. - Innovation Catalyst
With a focus on outcomes, service providers are incentivised to innovate and find new ways to achieve the desired results, driving continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Outcome-based services represent a transformative shift in the service business model, emphasising the achievement of tangible business results for customers. By aligning services with the broader objectives of customers, providers can deliver more impactful solutions, fostering deeper partnerships and driving mutual success in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Overall Business Model
Product-as-a-service - Prioritising Access Over Ownership
Background
Traditionally, businesses and consumers purchased equipment outright, bearing the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, upgrades, and eventual replacement. While this model offered complete control over the equipment, it also came with significant upfront costs and the responsibility of managing the asset's entire lifecycle.
The Product-as-a-Service Approach
Shifting from ownership to access, the Product-as-a-Service (PaaS) model allows businesses and consumers to access and use equipment without owning it. This can take various forms, from leasing and renting to comprehensive fleet management offerings. Customers gain the benefits of the equipment while the service provider takes on the responsibilities of maintenance, upgrades, and ensuring optimal performance.
Benefits
Adopting the PaaS model presents several compelling advantages:
- Financial Flexibility
Customers can avoid hefty upfront costs, paying only for the equipment's usage or access, which can be especially beneficial for expensive machinery. - Optimised Availability
With fleet management offerings, providers ensure that equipment is available when and where needed, maximising operational efficiency. - Reduced Maintenance Burden
The service provider typically handles maintenance, repairs, and upgrades, ensuring the equipment remains in top condition. - Scalability
As business needs change, customers can easily scale their equipment usage up or down without the constraints of ownership. - Sustainability
PaaS models can lead to more sustainable practices, as equipment is often used more efficiently, reducing waste and the need for production.
Conclusion
The Product-as-a-Service model revolutionises the traditional business approach, emphasising equipment access and availability over outright ownership. By providing flexible and efficient equipment solutions without the burdens of ownership, PaaS is setting a new standard in how businesses operate and grow in today's dynamic market landscape.
Outcome-as-a-service - Outsourcing for Guaranteed Results
Background
In traditional business models, companies invest in equipment and manpower to achieve desired outcomes, bearing full responsibility for operations, maintenance, and results. While offering control, this approach also came with the challenges of managing complex processes, ensuring equipment uptime, and bearing the risks associated with operational inefficiencies.
The Outcome-as-a-Service Approach
Transitioning from a focus on equipment to results, the Outcome-as-a-Service (OaaS) model allows companies to outsource entire operations or processes to a service provider. The provider supplies and manages the necessary equipment and delivers the specified outcome. The customer, in turn, is freed from operating the equipment and can focus on their core business, assured of the results they've contracted for.
Benefits
Embracing the OaaS model offers a range of advantages:
- Guaranteed Results
Customers pay for outcomes, ensuring they receive the desired results without operational hassles. - Operational Efficiency
With their expertise, service providers can often achieve higher levels of efficiency and performance, ensuring optimal results. - Cost Predictability
With a focus on outcomes, costs become more predictable, allowing for better budgeting and financial planning. - Risk Mitigation
By outsourcing, companies transfer operational risks to the service provider, ensuring any challenges or disruptions are managed effectively. - Focus on Core Business
Companies can concentrate on their primary business functions, leaving specialised operations to experts.
Conclusion
The Outcome-as-a-Service model represents a significant shift in business thinking, moving from equipment-centric operations to results-driven outsourcing. By entrusting specialised service providers to deliver guaranteed outcomes, companies can achieve better results, reduce risks, and maintain a sharper focus on their core business objectives in an increasingly competitive market.
Free Download
The Complete Guide
Everything you need to accelerate and maintain your pace in your service transformation.
Why is service transformation important for manufacturers?
The manufacturing industries are on an exciting journey, compelled to adapt and innovate due to several key trends:
- Intense Global Competition
Manufacturers worldwide are continually improving, leading to commoditisation and mounting pressure on margins. It's a race to deliver the best, the quickest. - Digital Disruption
The digital revolution is transforming customer expectations and behaviours. Traditional business models are being shaken up, and those who fail to adapt risk becoming obsolete. - Sustainability Imperative
Increasing global awareness of environmental issues presents new opportunities and challenges. Sustainable practices are no longer optional but a core expectation from customers and stakeholders.
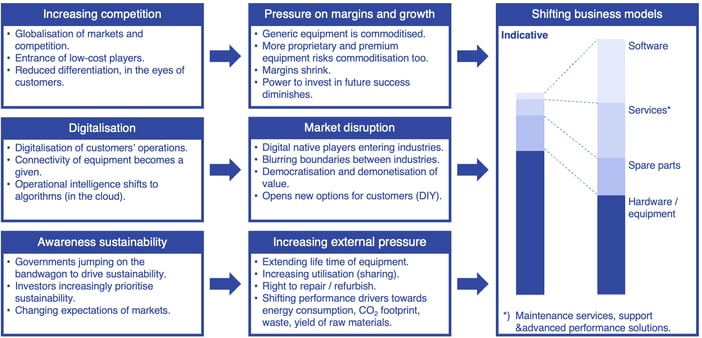
With industries rapidly transforming digitally and in services, there's a widening gap between the frontrunners and the laggards.
Laggards experience:
- The risk of overlooking critical opportunities, letting potential growth escape.
- The threat of being overshadowed by competitors.
- A declining trust and confidence from your stakeholders and teams.
- Operations trapped in the outdated mode of business-as-usual, even as the industry moves forward.
- Struggles to attract and retain talents.
- Struggles to attract and retain good investors.
However, the frontrunners are best positioned to experience:
- Accelerated growth.
- Staying ahead of (new) competition.
- Meeting the expectations of your stakeholders.
- Meeting the changing needs of your customers.
- Gaining and sustaining strategic commitment.
- Building confident and engaged teams.
- Attracting the best talents.
- Attracting the best investors.
The bottom line: Enriching business models with innovative services and software is becoming a critical factor for success. The service transformation is not just a strategic option—it's a vital move for the survival and growth of your business.
moreMomentum's Service Transformation Framework
The Service Transformation Framework is a strategic tool tailored for the leadership and innovation teams within B2B manufacturing companies.
This framework is a comprehensive guide to establish and sustain a high pace in service transformation endeavours.
It covers:
- Winning service strategies.
- Value propositions.
- Essential service business capabilities.
For each of these components, the framework offers insights into
- Best practices
- Emerging practices
- Maturity levels aligned with different stages of the transformation roadmap.
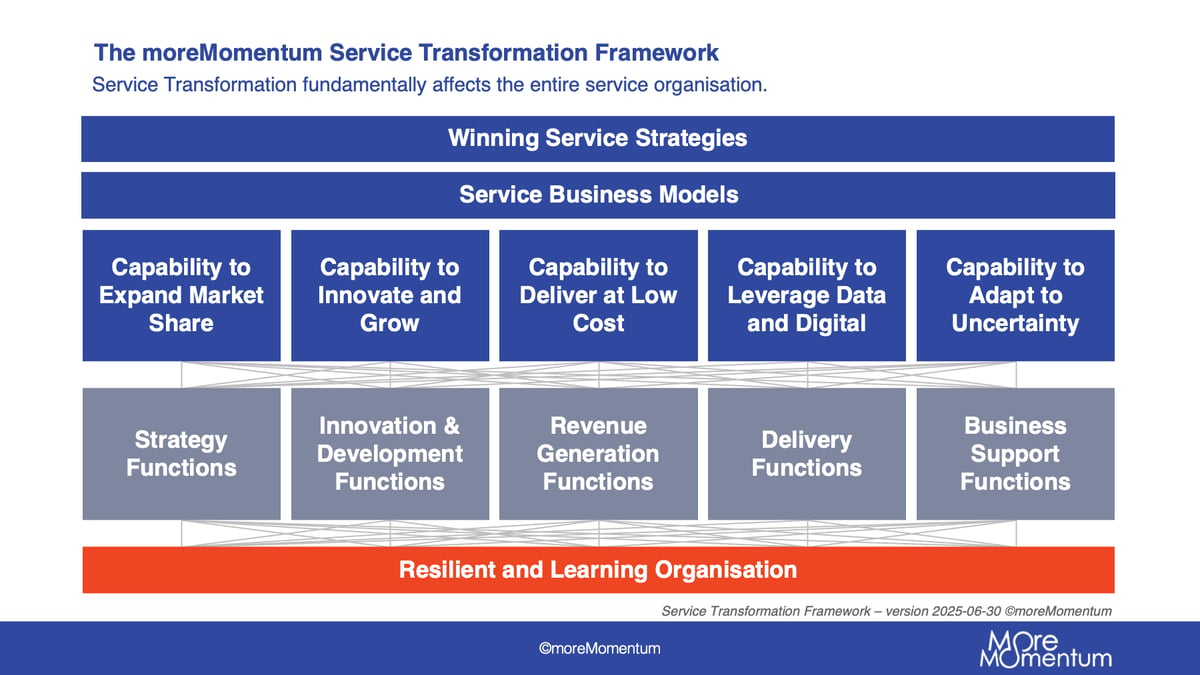
The Service Transformation process
Many service leaders grapple with the initial steps of the transformation journey, uncertain of the sequence and priorities. While this chapter won't offer a one-size-fits-all solution, it does provide insights into crucial considerations and facets to guide your service transformation journey.
Understanding the Unique Journey
No Silver Bullet
Every service transformation journey is distinct. It's essential to understand that there isn't a universal blueprint that fits all scenarios. The path each company takes is influenced by many factors, including the nuances of their industry, the ever-changing demands of their customers, and the specific vision and strategy they've set for themselves.
Embracing this uniqueness is the first step in crafting a successful transformation strategy.
Industry-Specific Factors
The industry in which a company operates plays a pivotal role in shaping its service transformation journey. Each industry comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities.
Whether it's the rapid technological advancements in the tech sector or the stringent regulatory requirements, these industry-specific factors can significantly impact how a company approaches its transformation.
By understanding these factors deeply, companies can tailor their strategies to address the specific hurdles better and leverage the unique opportunities their industry presents.
Organisational Capabilities vs. Value Proposition
Capability Development First
Before diving headfirst into the lucrative world of new service offerings, it's paramount for companies to lay a solid foundation. This often means prioritising the development of internal capabilities.
Whether it's training staff, investing in new technologies, or refining processes, these foundational steps ensure that when the time comes to roll out new services, the organisation is well-equipped to deliver them with excellence.
It's about ensuring the company can promise value and consistently deliver on it.
Monetising through Value Proposition
With robust capabilities in place, the next step is to translate them into tangible value for customers.
This is where crafting a compelling value proposition comes into play. A strong value proposition speaks directly to the evolved needs and desires of the customers, offering solutions that resonate with their pain points and aspirations.
But beyond just identifying these value points, it's about packaging them in an appealing and monetisable way. It's a delicate balance of understanding customer needs, leveraging organisational strengths, and presenting them in a market-ready format that drives revenue.
Market Lifecycle for New Solutions
Understanding the current phase of your new service or solution in the market lifecycle is crucial to tailor the right approach for its successful development and growth.
Innovators
These are the trailblazers, the first to try out new services or solutions. They're willing to take risks and are driven by the novelty and potential of an offering.
For service providers, this group offers an opportunity to gather initial feedback and make refinements. Their experiences can help in identifying potential pitfalls and areas of improvement.
Early Adopters
Often seen as thought leaders, early adopters significantly influence their peers. They're quick to see the potential benefits of a new service and are more willing to adopt it than the broader market.
Engaging with early adopters can help in building credibility and gaining testimonials. Their endorsement can be instrumental in driving wider acceptance.
Early Majority
Representing a more significant segment of the market, the early majority is more deliberate in their decision-making. They often need to see evidence of a service's benefits before committing.
For providers, this stage is about showcasing success stories and demonstrating the tangible benefits of the service. Building trust and offering proof points become critical.
Late Majority
Typically more conservative, the late majority adopts new services once they've become well-established and widely accepted.
At this stage, service providers might focus on offering more standardised packages, leveraging the service's track record, and emphasising its reliability.
Laggards
The last to adopt, laggards are often resistant to change. They might only consider a new service when it becomes the norm, or their traditional methods are no longer viable.
Convincing this group might require more traditional marketing methods, emphasising long-term stability and the risks of not adopting the service.
Solution Maturity Progression
The journey of a new service or solution from conception to widespread adoption is marked by distinct stages of maturity. Each stage represents a critical milestone, and understanding this progression can help service providers navigate the challenges and opportunities that arise.
Idea Development
This is the genesis of the solution, where an initial concept is formed. It's about identifying a gap in the market and conceptualising a service that can fill it.
Engage in brainstorming sessions, market research, and initial discussions with potential users to shape the idea.
Launching MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
A rudimentary version of the service is introduced to a select group at this stage. The aim is to test the waters and gather early feedback.
Focus on core features that represent the essence of the service. Engage with initial users to understand their experiences and gather insights.
Problem-Solution Fit
Here, the emphasis is on ensuring that the service effectively addresses the problem it set out to solve.
Refine the solution based on feedback, ensuring it aligns closely with user needs and genuinely solves the identified issue.
Product-Market Fit
This stage is about gauging the broader market's response. It's a validation phase to see if the solution has widespread appeal.
Engage with a larger audience, gather data on adoption rates, and refine the offering based on broader market feedback.
New Service Introduction
With refinements made and confidence in the solution's market fit, it's time for an official launch.
Internally, focus on building the necessary capabilities, capacity, and resources to support the new service. Externally, roll out comprehensive marketing campaigns, onboard new users, and establish mechanisms to aid adoption.
Scaling and Maturing
As the service gains traction, the focus shifts to expanding its reach and continuously improving it.
Explore new market segments, gather ongoing feedback, and make iterative improvements using an agile approach to ensure the service remains relevant and competitive. Embrace the principles of agility with rapid iterations, feedback loops, and adaptability at its core.
Read more about Service Innovation in our
Ultimate Guide for Service Innovation
Adapting the Journey: An Agile Approach to Roadmap Development
Service transformation is a dynamic journey characterised by evolving landscapes, shifting priorities, and the continuous acquisition of new insights. A roadmap for this journey isn't a rigid blueprint but a flexible guide, adaptable to the ever-changing circumstances and learnings that arise.
Vision and Strategy
While the end goal might remain consistent, the strategies to achieve it may need recalibration.
Regularly revisit the strategic plan, adjusting based on feedback, market changes, and internal developments.
Stakeholder Support
As the journey progresses, stakeholder needs and perspectives might shift.
Maintain open communication channels, update stakeholders on progress, and adapt to their evolving needs and feedback.
Cultural Evolution
A culture of adaptability and resilience is vital, promoting an environment where change is embraced.
Encourage a mindset of continuous learning, where new experiences are seen as opportunities for growth and refinement.
Capability Development
The skills and tools required at the start might differ from those needed later in the journey.
Continuously assess organisational capabilities, introducing new training and tools as the transformation demands.
Market Evolution
The market is fluid, and staying attuned to its changes ensures relevance.
Stay engaged with the market, adapting offerings and strategies based on emerging trends and customer feedback.
Step-by-Step Progression
Each phase of the journey informs the next, with lessons learned at one stage guiding subsequent steps.
Adopt an agile approach, iterating the roadmap based on real-world experiences and insights, ensuring a responsive and effective transformation process.
Continuous Review and Refinement
The path to service transformation is not linear, and as the journey unfolds, it's essential to remain receptive to feedback and adapt. This section emphasises the importance of ongoing evaluation and the willingness to refine strategies and offerings based on real-world insights.
Feedback Loops
A proactive approach to gathering insights ensures that the team's and the customer's voices are heard and considered.
Implement regular check-ins, surveys, or feedback sessions to capture valuable input from various stakeholders.
Iterative Improvements
A commitment to enhancement, where feedback is collected and acted upon.
Analyse the feedback received, identify areas of improvement, and make necessary adjustments to services or processes.
Staying Agile
The ability to remain flexible and responsive, not overly attached to a set plan but willing to change direction when needed.
Foster a culture that values adaptability, ensuring the organisation can swiftly respond to new challenges or opportunities.
The need for a high pace
In today's dynamic business landscape, the speed and efficacy with which organisations adapt and transform their services can mark the difference between market leadership and a gradual decline, potentially ending in obsolescence.
Maintaining a winning pace in service transformation is no longer merely a strategic advantage; it's a fundamental necessity.
As industries evolve and customer expectations shift, companies must continuously reinvent their service offerings to stay relevant and competitive.
The challenge lies in initiating change and sustaining momentum, ensuring that the transformation journey aligns with the rapid pace of external changes.
How to increase and maintain your pace
Service transformation is a long-term journey, often spanning years or even decades. The following key factors can accelerate and maintain your pace during the service transformation journey.
Define Your Strategic Direction
- Craft Your Mission and Vision
Establish a clear and inspiring purpose for your organisation, outlining where you want to be in the future and what you stand for. - Develop a Winning Strategy
Align your strategy with organisational goals and market demands, ensuring your industry has a competitive edge. - Plan for Future Scenarios
Stay ahead by anticipating potential challenges and opportunities, ensuring your organisation remains adaptable in an ever-changing landscape. - Execute Your Strategy Effectively
Break down your strategic plans into actionable steps, monitor progress, and adjust as necessary to achieve your objectives.
Foster a Culture of Innovation
- Build Robust Innovation Capabilities
Ensure your organisation has the structures, processes, and mindset to generate and implement innovative ideas consistently. - Adopt Agile Methodologies
Embrace flexibility by implementing iterative approaches, allowing you to adapt swiftly to changes and deliver value continuously. - Manage Change Proactively
Implement structured strategies to navigate organisational changes, minimising disruptions and maximising buy-in. - Engage in External Collaborations
Form strategic partnerships to bring fresh perspectives, expertise, and opportunities for co-innovation.
Shape Your Organisational Dynamics
- Nurture the Right Culture & Mindset
Create an environment that is receptive to change, values service excellence and encourages innovative thinking. - Engage All Stakeholders
Foster open communication and collaboration, ensuring everyone from frontline staff to top management is aligned with your transformation vision. - Empower Service and Innovation Champions
Form and support dedicated teams that are equipped and motivated to drive your service transformation initiatives forward. - Prioritise Continuous Learning
Emphasise the ongoing development of your team, ensuring they have the skills and knowledge to excel in their roles.
Allocate Resources Strategically
- Optimise Resource Allocation
Ensure that time, budget, and personnel are effectively allocated to support and advance your transformation initiatives. - Balance Your Initiatives
Strategically distribute resources among short-term, mid-term, and long-term projects, ensuring a mix of immediate results and future growth.
Harness Knowledge and Gain Insights
- Stay Informed and Updated
Regularly update your knowledge base with the latest industry trends, insights, and best practices to inform your strategic decisions. - Implement Feedback Mechanisms
Establish systems to gather feedback from various sources, allowing you to measure success, gain insights, and refine your strategies based on real-world data.
The Pivotal Role of Leadership and Innovation Teams
The Cornerstone of Service Transformation
In service transformation, leadership and innovation teams are the most important groups. While many factors can push an organisation forward, the skills and knowledge of these teams are the base for all other efforts. Their experience, vision, and ability to change set the direction for the organisation's transformation journey.
Nurturing Core Competencies
But the potential of these teams can grow even more. Organisations must focus on their ongoing development to make the most of their abilities. This means regular training, creating a learning culture, and ensuring they have the latest knowledge and skills. By supporting the growth of leadership and innovation teams, organisations not only speed up their current transformation work but also set themselves up for success in the future.
Conclusion - The Imperative of a high pace
Service transformation is not a mere shift in operations; it's a profound evolution that reshapes the very essence of a business. As we've explored in this guide, the journey is intricate, demanding a blend of strategic foresight, innovative thinking, and unwavering commitment. Yet, at the heart of this transformation lies the competencies of leadership and innovation teams. Their knowledge, insights, and capabilities are the driving force that can either accelerate or hinder progress.
As you reflect on your organisation's service transformation journey, consider this: What are the biggest obstacles and challenges you currently face? And more importantly, what expertise, insights, and competencies could help you overcome them? Take a moment to assess these critical areas. By identifying and addressing these gaps, you position your organisation for temporary success and sustained excellence in an ever-evolving landscape. Dive deeper, learn continuously, and let this guide be your compass in the transformative journey ahead.
The Cornerstone of Service Transformation
In service transformation, leadership and innovation teams are the most important groups. While many factors can push an organisation forward, the skills and knowledge of these teams are the base for all other efforts. Their experience, vision, and ability to change set the direction for the organisation's transformation journey.
Nurturing Core Competencies
But the potential of these teams can grow even more. Organisations must focus on their ongoing development to make the most of their abilities. This means regular training, creating a learning culture, and ensuring they have the latest knowledge and skills. By supporting the growth of leadership and innovation teams, organisations not only speed up their current transformation work but also set themselves up for success in the future.
Free Download
The Complete Guide
Everything you need to accelerate and maintain your pace in your service transformation.
